Thai and Vietnamese: are they similar? which is harder to learn?
Did you know about half of all languages are tonal? This means the same word, said with two different tones, means two different things. Thai and Vietnamese are two of these tonal languages.
The two countries are close to each other, both in Southeast Asia. Despite this, the languages are somewhat different from one another.
So, is Thai harder or easier than Vietnamese? Vietnamese is an easier language to learn. Here’s why:
- the Vietnamese alphabet is much easier to learn than the Thai one.
- Vietnamese tones are easier to identify when reading
- Vietnamese and Thai grammar are similar
- Vietnamese and Thai tone pronunciation is equally difficult
The Thai alphabet is much harder to learn than the Vietnamese one
The Vietnamese and Thai alphabets have nothing in common. But, as it is based on the Latin alphabet, the Vietnamese alphabet looks more familiar to English speakers.
Interestingly, several centuries ago Vietnamese was written using Chinese characters. During Vietnam's era of French colonialism, a Latin script was developed for the Vietnamese language. This Latin-based script replaced the Chinese characters for writing Vietnamese.
The Vietnamese alphabet has 29 letters—12 vowels and 17 consonants. Most of the letters are the same as in English. They make slightly different sounds, though.
The Vietnamese alphabet does have a few letters that don’t exist in the Latin alphabet: for instance, the letter «đ».
In contrast, the Thai alphabet is completely unrelated to our familiar Latin alphabet. The Thai alphabet contains a total of 72 characters—44 consonants and 28 vowels. This is over twice the number of letters in Vietnamese.
Some of the Thai characters look very similar, and can be distinguished only by noticing tiny differences. So learning the Thai alphabet requires a lot of rote memorization and the use of flashcards.
Which is easier to read: Vietnamese or Thai?
Vietnamese and Thai are both written and read left to right. This part comes naturally to English speakers.
There is one key difference between reading Vietnamese and reading Thai, though. Let’s look at both below.
- English: Do you want to go to the movies?
- Vietnamese: Bạn có muốn đi xem phim không?
- Thai: คุณต้องการที่จะไปดูหนัง?
The Vietnamese sentence is difficult to read. But, you would be close by using the sounds in English.
Thai, on the other hand, can't be read at all. The only way to read the Thai sentence is to have a working knowledge of its alphabet already.
How easy is it to read Vietnamese?
Many Vietnamese letters are similar to their English counterpart, with a slight adjustment to the pronunciation.
There are 12 vowels in Vietnamese. Here are their different sounds.
- a ( fat )
- ă (cut)
- â (person)
- e ( pet )
- ê (may)
- i/y ( bee)
- o (saw)
- ô (joke)
- ơ (curd)
- u (shoo)
- ư (good)
There is only one consonant that doesn’t exist in English, «đ». It makes the 'd' sound we are used to in English.
- đ (do)
- d (zoo)
Learning to read Vietnamese is not difficult for beginners. The unfamiliar vowels take extra practice. The use of the Latin alphabet allows beginners to start reading in a short time.
How easy is it to read Thai?
It takes longer to learn to read Thai compared to learning to read Vietnamese. It is a whole new alphabet to learn. And none of the characters look like English letters. In addition, there are sounds in Thai that don't exist in English.
Common Thai Consonants
- ก (gun)
- ข (kid)
- ค (king)
- ง (sing)
- จ (jam)
Common Thai Vowels
- ไอ/ใอ (high)
- อำ (sum)
- เอา (chow)
- เอีย (chia)
The character, « อ », is a placeholder. Either it would stay like this, and the speaker would only pronounce the vowel sound. Or it would be replaced with another consonant.
Another thing to know is the placement of Thai vowels. You can find them all around the consonants. Above, below, before, and after the consonants. Look at these examples. Remember: « อ » is a placeholder.
- Thai vowel above the consonant:
Word: ปี (bpee)
Meaning: year
Vowel: อี (ee — long) - Thai vowel below the consonant:
Word: งู (ngoo)
Meaning: snake
Vowel: อู (oo — long) - Thai vowel before the consonant:
Word: เวลา (weehh-laa)
Meaning: time
Vowel: เอ (eehh — long) - Thai vowel after the consonant:
Word: มา (maa)
Meaning: come
Vowel: อา (aa — long) - Thai vowels before and after the consonant:
Word: เกาะ (gawh)
Meaning: island
Vowels: เอาะ (awh — short) - Thai vowels before, after and above the consonant:
Word: เรียน (rian)
Meaning: learn
Vowels: เอีย (ia — long)
This provides a significant barrier to reading as beginners adjust.
One thing is essential to mention. Northern and Southern Thai are different from each other. So different that people from the north and south have difficulty understanding each other.
However, Central Thai is the official language. And people from the north and south can understand Central Thai.
Northern Thai has its own writing system, too.
Thai
Thai
This won’t impact a student’s learning. But a student may encounter it when traveling through Northern Thailand.
Vietnamese tones or Thai tones: which are easier to master when reading?
Vietnamese makes it easy to read the tonal system. In Thai, it's going to be more challenging to figure out the tone.
In Vietnamese, there are five tonal markers. These tell precisely the tone to use. It’s as simple as remembering the tone markers.
In Thai, it is more complicated. There are more things to take into factor to get the correct tone.
Let’s look at examples of how Vietnamese and Thai tones are different.
List of Vietnamese tones
Tone name: ngangTone Type: high, flat tone
Marking: none
Example: ma (ghost) Tone name: huyền
Tone Type: starts low, stays low
Marking: `
Example: mà (which, that) Tone name: sắc
Tone Type: starts high, goes higher
Marking:’
Example: má (mother; cheek) Tone name: nặng
Tone Type: short and low tone
Marking: .
Example: mạ (rice seedling) Tone name: hỏi
Tone Type: tone rises, like asking a question
Marking: ̉
Example: mả (tomb) Tone name: ngã
Tone Type: tone rises but is cut short
Marking: ~
Example: mã (horse)
Thai Tones
Word: จาน (jaan - plate)Tone Type: Mid-tone Word: ก่อน (gorn - before)
Tone Type: Low tone Word: บ้าน (baan - house)
Tone Type: falling Word: ร้อน (ron - hot)
Tone Type: high Word: หมา (maa - dog)
Tone Type: rising
Thai has tone markers as well. They do not have a simple system to follow, though. Here are the Thai tones and their names.
- ่ (mái-èek)
- ้ (mái-too)
- ๊ (mái-dtrii)
- ๋ (mái-jàt-dtà-waa)
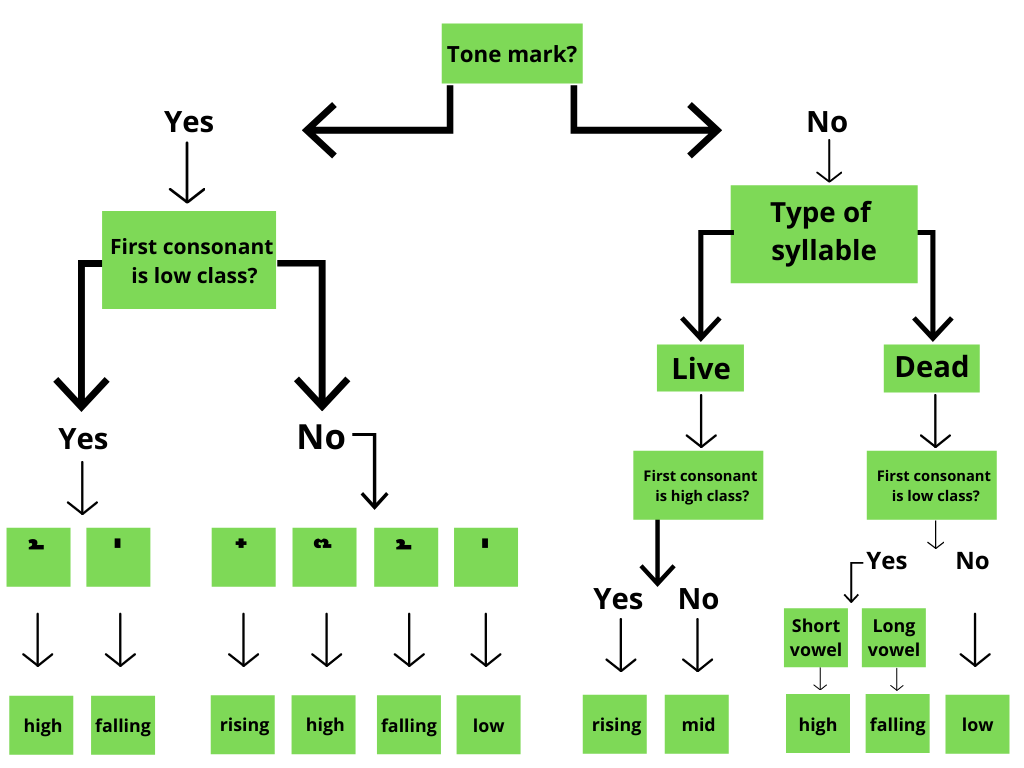
Three things determine the tone of a word in Thai.
- First consonant class (low, middle, high)
- Tone markers ( ่, ้, ๊, ๋)
- Ending type (live or dead)
Once we find these, we have one of the five tones in Thai. There are rules to follow to know the tone, but it is beyond the scope of this article.
This chart is a helpful introduction and resource to use.
Learning Vietnamese and Thai grammar
Thai and Vietnamese grammar is easy for English speakers when starting out. They both follow the same structure as English.
- English: I eat rice every day.
- Vietnamese: Tôi ăn cơm hàng ngày.
- Transliteration: Toi an kerm hang ngai
- Thai: ผมกินข้าวทุกวัน
- Transliteration: Pom gin khaao tuk waan
All three languages follow a subject + verb + object sentence structure.
Where Thai and Vietnamese are different from English is tenses. English has 12 tenses in total. Thai and Vietnamese have none. This is one less thing for learners to worry about when learning the languages.
No tenses in Vietnamese and Thai makes it easy
Instead of tenses, both languages show the time something was done using time words. These words are placed after the verb, usually to show the time of an action.
Let’s look at examples.
Useful Vietnamese and Thai past-time words
Already- Vietnamese: đã (da)
- Thai: แล้ว (laew)
- Vietnamese: hôm qua (hom gwaa)
- Thai: เมื่อวาน (muea waan)
- Vietnamese: năm ngoái (nam waai)
- Thai: ปีที่แล้ว (bpee tee laew)
Useful Vietnamese and Thai present-time words:
To show a continuous action- Vietnamese: đang (dahng)
- Thai: กำลัง (gam-lang)
- Vietnamese: hôm nay (hom nay)
- Thai: วันนี้ (wan-nee)
- Vietnamese: bây giờ (bai zer)
- Thai: ตอนนี้ (dtorn-nee)
Useful Vietnamese and Thai future time words
Will- Vietnamese: sẽ (seh)
- Thai: จะ (ja)
- Vietnamese: ngày mai (ngai mai)
- Thai: พรุ่งนี้ (prueng nee)
- Vietnamese: năm sau (nam sao)
- Thai: ปีหน้า (bpee naa)
Words in both languages share similar patterns. For example, Thai uses «นี้» (nee) when talking about "this one".
-
ตอนนี้ (dtorn nee) — now
Literal translation: at - this (moment) -
วันนี้ (wan nee) — today
Literal translation: day - this -
เดือนนี้ (duean nee) — this month
Literal translation: month - this
Vietnamese does the same with the word «nay».
-
hôm nay (hom nai) — today
Literal translation: day - this -
tháng này (tang nai) — this month
Literal translation: month - this -
Năm này (nam nai) — this year
Literal translation: year - this
How do I ask questions in Vietnamese and Thai?
Questions in Vietnamese and Thai have similarities. For example, Thai places question words at the end of the sentence. The same applies to Vietnamese.
Let’s look at an example. Here is how we can ask how much something costs.
Vietnamese: Chi phí bao nhiêu?Transliteration: Chi fee bao niew
Literal translation: Expense - how - much?
Question word: bao nhiêu (how much/many) Thai: ราคาเท่าไหร่คะ?
Transliteration: raakaa tao rai ka? (Female speaker)
Literal translation: Price - how - much?
Question word: เท่าไหร่ (how much — price)
Both of the question words are at the end of the sentences. In Vietnamese, the question word can go at the beginning, too.
Vietnamese: Tại sao bạn thích đến thăm Việt Nam?Transliteration: Tai são ban tick duen tham Vietnam?
Literal translation: Why - you - like - visit - Vietnam?
Question word: Tại sao (why) Vietnamese: Khi nào bạn đi Hà Nội?
Transliteration: Nee nao ban dee Hanoi?
Literal translation: When - do - you - go - Hanoi?
Question word: Khi nào (when)
How do I make negative sentences in Vietnamese and Thai?
Creating negative sentences in both Vietnamese and Thai is easy. It’s as simple as putting ‘no’ in front of the main verb.
In Thai, this word is «ไม่». In Vietnamese, it is «không».
Vietnamese: Tôi không thích hải sản.Transliteration: Dtoi kong tick hai saan.
Literal translation: I - no - like - seafood.
Thai: ฉันไม่ชอบอาหารทะเลคะ.
Transliteration: Chan mai chob aa-haan ta-lay ka. (Female speaker)
Literal translation: I - no - like - food - sea.
This aspect of grammar is beginner-friendly, both in Thai and in Vietnamese. No need to worry about contractions or the placement of the negative part. Once we find the main verb, we can easily make negative sentences.
Thai vs. Vietnamese pronunciation
Vietnamese and Thai both have tones, and they’re both difficult to learn.
Both languages rely on tones for word meaning. This is the most challenging area for beginners.
Vietnamese has 6 tones. Some people say Vietnamese has eight tones. This is because of minor differences in individual tones. But officially, there are six tones.
If a learner is coming from a language with no tones, more practice is vital.
Thai tones are easy to hear once a learner immerses themselves in the language. The tones are distinguishable. So there won’t be an issue confusing them.
Now, let’s look at how the pronunciation of the tones changes the meaning.
This is where foreigners end up looking silly but in a good way!
Here are some examples of Vietnamese tones:
Here are some examples of Thai tones:
Each language has its share of similar-sounding words. It’s part of the fun of learning a language. You will look and feel embarrassed, but you learn from it.
And, besides, native speakers are happy you’re trying. The effort is enough for them.
Conclusion
As with every language, it’s going to come down to determination. If a learner puts in the hours, they’ll get a quicker return.
Vietnamese is easier than Thai. The use of the Latin alphabet is easier to learn and start reading.
The pronunciation and grammar are similar and take an equal amount of time to learn. The Thai alphabet has a more significant learning curve and therefore takes longer.
And, during that time, a learner could be advancing in Vietnamese at a faster rate.
